INTRODUCTION
In cells and tissues, the histone proteins that constitute the nucleosomes can present multiple post-translational modifications, such as lysine acetylation, lysine and arginine methylation, serine phosphorylation, and lysine ubiquitination. On their own, or in combination, these covalent modifications on the core histones are thought to play essential roles in chromatin organization and gene expression in eukaryotes. Importantly, patterns of histone modifications may be somatically conserved and can, thereby, maintain locus-specific repression/activity in defined lineages, or throughout development. Indirect immunofluorescence studies on cultured cells have been pivotal in unraveling the roles of histone modifications. However, to address in detail what happens at specific sites in vivo, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) is the method of choice. Here, we describe how ChIP can be performed on non-fixed chromatin from animal cells or tissues (fresh or frozen) to analyze histone modifications at specific chromosomal sites. These protocols are suitable only for analyzing histones and their modifications. For other applications, chromatin immunoprecipitation should be performed on cross-linked chromatin.
RELATED INFORMATION
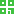
This ChIP protocol was derived from methodologies originally described by O’Neill and Turner (1995). It was published earlier on the Web site of the European Network of ExCellence "EPIGENOME" (www.epigenome-noe.net), and was adapted from Umlauf et al. (2003). An overview of the procedure is provided in Figure 1 . Following ChIP, we use different PCR-based methods that allow one to analyze a locus of interest in the precipitated chromatin.
染色体免疫共沉淀法(ChIP)分析细胞和组织中未固定染色体中组
View larger version (16K):Figure 1. Flowchart of the procedures used to investigate site-specific covalent modifications (i.e., methylation and acetylation) on histones. In summary, nuclei are purified from fresh/frozen tissues or from cells, and the chromatin, after fractionation with micrococcal nuclease (MNase), is purified from the nuclei. This "input chromatin," made up of fragments of up to seven nucleosomes in length, is incubated with an antiserum directed against the histone modification of interest. The antibody-bound fraction is separated from the unbound fraction and, after extraction of genomic DNA from the bound and unbound fractions, PCR technologies are applied to specifically analyze the gene or chromosomal region of interest. Precipitated DNAs can be used as probes to hybridize DNA tiling arrays (ChIP on chip) as well.
免责声明
- 凡本网注明“来源:化工仪器网”的所有作品,均为浙江兴旺宝明通网络有限公司-化工仪器网合法拥有版权或有权使用的作品,未经本网授权不得转载、摘编或利用其它方式使用上述作品。已经本网授权使用作品的,应在授权范围内使用,并注明“来源:化工仪器网”。违反上述声明者,本网将追究其相关法律责任。
- 本网转载并注明自其他来源(非化工仪器网)的作品,目的在于传递更多信息,并不代表本网赞同其观点和对其真实性负责,不承担此类作品侵权行为的直接责任及连带责任。其他媒体、网站或个人从本网转载时,必须保留本网注明的作品第一来源,并自负版权等法律责任。
- 如涉及作品内容、版权等问题,请在作品发表之日起一周内与本网联系,否则视为放弃相关权利。
 手机版
手机版 化工仪器网手机版
化工仪器网手机版
 化工仪器网小程序
化工仪器网小程序
 官方微信
官方微信 公众号:chem17
公众号:chem17
 扫码关注视频号
扫码关注视频号





















 采购中心
采购中心