详细介绍
干细胞不同基底硬度机械力培养系统

特别适合细胞、干细胞不同基底硬度牵张拉伸刺激培养或静态培养(模量刚度范围1-80 kPa)。
美国flexcell提供CellSoft™型号的不同基底硬度培养耗材包括:不同基底硬度牵张拉伸培养板、培养皿和可用于显微观察的腔室载玻片(圆形多孔板)多种不同的种类,该cellsoft不同基底硬度培养耗材共价包被Collagen I或其他蛋白配合flexcell细胞牵张拉伸培养仪,可对细胞进行静态或动态牵拉应力刺激。更重要的一点,新型的CellSoft™ 培养板可以反复胰酶消化和再接种细胞,蛋白包被的表面可以重复使用多达三次。
美国Flexcell公司专注于细胞组织应力(牵张拉伸应力、三维水凝胶牵张拉伸应力、压应力和流体切应力等)加载刺激培养产品的设计和制造,提供*的体外细胞拉应力、压应力和流体剪切应力加载刺激与立体水凝胶支架三维细胞组织牵拉加载培养系统而*。

其产品成熟度高、成功应用文献量达4000多篇,国内有包括上海交通大学、复旦大学、同济大学、上海第九医院、中科院力学所、北京大学第三医院、北航生物与医学工程学院、都医科大学、广州医科大学、南方科技大学、福建协和医院、南方医科大学近100家成功高校、医院及基础科研单位使用,无技术风险和使用风险,flexcell体外高通量细胞牵张拉伸力、压应力以及流体剪切力加载培养系统已成为细胞力学体外加载模型的黄金标准,是细胞组织力学研究者的shou选。
FX-5000T细胞牵张拉伸应力加载系统(Flexcell FX5000 Tension system)

系统基本原理(负气压交换模式):
橡胶密封垫在细胞培养板基底膜与基板之间形成封闭腔,把此密封腔的进、出气管插入二氧化碳培养箱里,把此密封腔放入二氧化碳培养箱, 利用封闭腔抽真空产生的负压使弹性基底膜(拉动三维支架)发生形变,通过计算机控制系统调节气体的压力来改变基底膜的形变量,进而使贴壁生长的细胞受到牵拉加载刺激。
亮点:
1)该系统对二维、三维细胞和组织各种培养物提供轴向和圆周应力加载;不但具有双轴向拉伸力加载,还具备单轴向加力功能
2)计算机控制的应力加载系统,为体外培育的细胞提供的、可控制的、可重复的、静态的或者周期性的应力变化。
3)使用真空泵,抻拉培养板底部的弹性硅胶模,细胞培养板底部伸展度可达到33%,通过气体装置可以自动调节和控制应力。
4)基于柔性膜基底变形、受力均匀;
5)可实时观察细胞、组织在应力作用下的反应;
6)*的flexstop隔离阀可使同一块培养板力的一部分培养孔的细胞受力,一部分培养孔的细胞不受力,方便对比实验;
7)与压力传导仪整合,同时兼备多通道细胞压力加载功能;
8)与Flex Flow平行板流室配套,可在牵拉细胞的同时施加流体切应力;
9)多达4通道,可4个不同程序同时运行,进行多个不同拉伸形变率对比实验;
10)同一程序中可以运行多种频率,多种振幅和多种波形;
11)加载模拟波形种类丰富:静态波形、正旋波形、心动波形、三角波形、矩形以及各种特制波形;
12)更好地控制在超低或超高应力下的波形;
13)电脑系统对牵张拉伸力加载周期、大小、频率、持续时间智能调控
14)加载分析各种细胞在牵张拉应力刺激下的生物化学反应
15)伸展度范围广:0-33%
16)牵拉频率范围广:0.01-5Hz
17)典型应用:
该系统感应各种细胞在应力刺激下的生物化学反应,例如:骨骼细胞,肺细胞,心肌细胞,血细胞,皮肤细胞,
肌腱细胞,韧带细胞,软骨细胞和骨细胞等各种2D或3D细胞组织。
典型应用科室:
| 口腔 | 颞下颌关节滑膜细胞、人牙周膜细胞、口腔上皮细胞、口腔鳞癌KB细胞等 |
| 骨: | 骨骼细胞、肌腱细胞、韧带细胞、软骨细胞和骨细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞, 软骨组织、椎间盘骨组织、肌腱组织、韧带组织等 |
| 肺呼吸 | 肺细胞、肺上皮细胞、肺动脉内皮细胞、人肺微血管内皮细胞 |
| 眼科视觉神经 | 眼上皮细胞、眼小梁组织细胞、视网膜神经细胞 |
| 心血管/高血压: | 心肌细胞、血细胞、心血管平滑肌细胞、血管内皮细胞 |
| 生殖 | 肾膀胱细胞、平滑肌细胞/尿路上皮及尿路上皮细胞、肾小管上皮细胞 |
| 消化 | 肠上皮细胞、 胃上皮细胞、胃血管内皮细胞 |
| 皮肤 | 皮肤细胞、皮肤成纤维细胞 |
2、FX-5000C细胞压力加载系统(flexcell FX5000 Compression system)——提供样机体验

系统基本原理(正气压交换模式):
利用橡胶密封垫在细胞培养板基底膜与基座之间形成封闭腔,把此密封腔的进、出气管插入二氧化碳培养箱里,把此密封腔放入二氧化碳培养箱,利用封闭腔正气压挤压培养孔里的活塞,进而使活塞和固定台之间的凝胶三维培养物间接受到压力发生形变,通过计算机控制系统调节气体的压力来改变基底膜的形变量。
(注释:压力加载培养板每个培养孔里都有一对活塞或固定台)
亮点
1)该系统对各种组织、三维细胞培养物提供周期性或静态的压力加载;
2)基于柔性膜基底变形、受力均匀;
3)可实时观察细胞、组织在压力作用下的反应;
4)可有选择性地封阻对细胞的应力加载;
5)同时兼备多通道细胞牵拉力加载功能;
6)多达4通道,可4个不同程序同时运行,进行多个不同压力形变率对比实验;
7)同一程序中可以运行多种频率(0.01- 5 Hz),多种振幅和多种波形;
8)更好地控制在超低或超高应力下的波形;
9)多种波形种类:静态波形、正旋波形、心动波形、三角波形、矩形以及各种特制波形;
10)电脑系统对压力加载周期、大小、频率、持续时间智能调控
11)压力范围:0.1 - 14磅,夹在活塞和固定台之间的BioPress细胞培养板可承受正压力0.1---14磅
12)典型应用科室:
检测各种三维细胞组织在压力作用下的生物变化、反应,
例如:软骨组织,椎间盘骨组织,肌腱组织,韧带组织,以及从肌肉,肺,心脏,血管,皮肤,肌腱,韧带,软骨和骨中分离出来的细胞。
13)在智能电脑主机的控制下,压力传导仪内的密封阀门装置自动调节和控制压力。
14)系统具有模块化易升级,可扩展拉应力加载、流利切应力加载、三维细胞组织培养功能。具有细胞组织力学所要求的所有类型:牵张拉伸力、压力、流体切应力加载刺激功能。
15)通过StagePress显微压应力加载设备,实时观察细胞、组织在拉/压应力作用下的反应
3、全自动可牵张拉伸刺激立体水凝胶支架三维细胞培养系统(Flexcell TissueTrain System)——提供样机体验
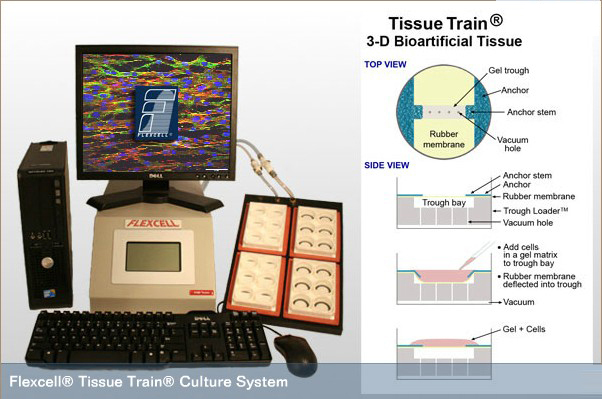
| FLEXCELL Tissue Train®是个独立的全自动细胞组织三维培养、组织构建计算机智能控制的生物反应器系统,它允许研究者创建三维基质凝胶支架, |
| 真正意义上的三维培养——该系统以多种包被表面(Amino、Collagen (Type I or IV)、Elastin、 ProNectin (RGD)、Laminin (YIGSR))的水凝胶为细胞外基质支架——水凝胶支架因在液态时包裹细胞,固态时形成交联网络,细胞粘附力强,良好水分、养分交换。 水凝胶是一种状似果冻的物质,具有高弹性、吸水性的聚合物组成的网状物,用于组织工程中,作为帮助细胞生长和发展的支架. 利用立体水凝胶支架作为平台,观察不同细胞的交互作用,建立组织和器官。同时通过在立体环境中培育细胞,有助于更深入地了解细胞过程和交互作用. 在基质里细胞培养、构建生物组织,可为三维细胞、组织提供双轴向应力和单轴向应力,FLEXCELL Tissue Train® |
是当今科研界的可拉伸刺激三维细胞培养、生物组织构建系统。 4\多流场六通道流体切应力培养与实时观察系统
|
二、excellness代理,PrimeCoat弹性基底培养皿板
PrimeCoat series
The ExCellness PrimeCoat series is designed specifically to provide a biomimetic cell culture environment that improves cell characteristics and phenotype in laboratory applications.

Key features
- PrimeCoat elastic substrates are easy to use for cell culture and subsequent analysis.
- PrimeCoat elastic substrates are available with 6 degrees of softness within the elasticity range of body tissues: 2, 5, 10, 15, 30 and 100 kPa.
- PrimeCoat elastic substrates are available in 4 standard formats: 100 mm diameter dishes, 40 mm diameter dishes, 24-well plates and 20x20 mm cover slips.
- PrimeCoat elastic substrates require to be coated by the end user to promote cell adhesion.
- PrimeCoat elastic substrates are transparent. Cells can be visualized with standard transmission light microscopes (e.g., Phase contrast, DIC).
- PrimeCoat elastic substrates are compatible with most standard molecular or cellular techniques: immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry, protein analysis (e.g., Western blotting, and RNA/DNA extraction).
Biomimetic cell culture substrates at reach
PrimeCoat series combines simplicity and accessibility:
- simplicity of cell handling
- straightforward compatibility with cell analysis tools
- accessible prices
ExCellness in selected peer reviewed publications
In the following peer-reviewed publications, ExCellness biomimetic cell culture devices have been used or cited:
- A Glentis et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce metalloprotease-independent cancer cell invasion of the basement membrane. Nat Commun. 2017 Oct 13;8(1):924.
- N Vedrenne et al. Isolation of astrocytes displaying myofibroblast properties and present in multiple sclerosis lesions. Neurochem. Res. 2017 Apr 22.
- X L Chen et al. MicroRNA-21 preserves the fibrotic mechanical memory of mesenchymal stem cells. Nature Materials 16, 379–389 (2017).
- MR Zeglinski et al. Chronic expression of Ski induces apoptosis and represses autophagy in cardiac myofibroblasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2016 Jun;1863(6 Pt A):1261-8.
- H Chen et al. Mechanosensing by the α6-integrin confers an invasive fibroblast phenotype and mediates lung fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2016 Aug 18;7: 12564.
- NP Talele et al. Expression of α-Smooth Muscle Actin Determines the Fate of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Stem Cell Reports. 2015 Jun 9;4(6) : 1016-30.
- V Sarrazy et al. Integrins avb5 and avb3 promote latent TGF-beta 1 activation by human cardiac fibroblast contraction. Cardiovasc Res (2014) 102 (3)
- VF Achterberg et al. The nano-scale mechanical properties of the extracellular matrix regulate dermal fibroblast function.J Invest Dermatol. 2014 Jul;134(7):1862-72.
- JA Cadby et al. Differences between the Cell Populations from the Peritenon and the Tendon Core with Regard to Their Potential Implication in Tendon Repair. 2014. PLoS ONE 9(3): e92474.
- T. Grand et al. Aggravation of Cardiac Myofibroblast Arrhythmogeneicity by Mechanical Stress. Cardiovasc Res. 2014 Dec 1;104(3):489-500.
- JA Cadby. Can we improve tendon healing in the horse? A multi-angle study of a multi-facet problem. ISBN: 978-90-5335-715-6.
- A Vashist et al. Recent advances in hydrogel based drug delivery systems for the human body. J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 147-166.
- EP van der Veer et al. The RNA-Binding Protein Quaking is a Critical Regulator of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotype. Circ Res. 2013 Oct 12;113(9):1065-75.
- A De Boeck et al. Differential secretome analysis of cancer-associated fibrobroblasts and bone marrow-derived precursors toidentify microenvironmental regulators of colon cancerprogression. Proteomics 2013,13,379-388.
- C Godbout et al. The Mechanical Environment Modulates Intracellular Calcium Oscillation Activities of Myofibroblasts.PLoS One. 2013; 8(5): e64560.
- S Constant et al. Colon Cancer: Current Treatments and Preclinical Models for the Discovery and Development of New Therapies. Drug discovery; Editor Hany A. El-Shemy. ISBN 978-953-51-0906-8.
- JL Balestrini et al. The mechanical memory of lung myofibroblasts. Integr. Biol., 2012,4, 410-421.
- Stem Cells and Cancer Stem Cells, Volume 8. Therapeutic Applications in Disease and Injury. Editors M.A. Hayat. ISBN 978-94-007-4797-5.
- A Skardal et al. Bioprinted amniotic fluid-derived stem cells accelerate healing of large skin wounds. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012 Nov;1(11):792-802. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2012-0088. Epub 2012 Oct 29.
- A Skardal et al. Substrate elasticity controls cell proliferation, surface marker expression and motile phenotype in amniotic fluid-derived stem cells. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2013 January; 17: 307-316.
- BJ Crider et al. Myocardin-Related Transcription Factors A and B Are Key Regulators of TGF-b1-Induced Fibroblast to Myofibroblast Differentiation. Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2011) 131, 2378-2385.
- L Follonier Casla et al. A new lock-step mechanism of matrix remodelling based on subcellular contractile events. Journal of Cell Science 123, 1751-1760.
订货信息:
Dishes
Product Code Description
01. 100.002.00 2 kPa culture surface 100 mm ø
01. 100.005.00 5 kPa culture surface 100 mm ø
01. 100.010.00 10 kPa culture surface 100 mm ø
01. 100.015.00 15 kPa culture surface 100 mm ø
01. 100.030.00 30 kPa culture surface 100 mm ø
01. 100.100.00 100 kPa culture surface 100 mm ø
Product Code Description
01. 035.002.00 2 kPa culture surface 35 mm ø
01. 035.005.00 5 kPa culture surface 35 mm ø
01. 035.010.00 10 kPa culture surface 35 mm ø
01. 035.015.00 15 kPa culture surface 35 mm ø
01. 035.030.00 30 kPa culture surface 35 mm ø
01. 035.100.00 100 kPa culture surface 35 mm ø
Multi-well plates
Product Code Description
04.024.002.00 2 kPa culture surface 24-well plate
04.024.005.00 5 kPa culture surface 24-well plate
04.024.010.00 10 kPa culture surface 24-well plate
04.024.015.00 15 kPa culture surface 24-well plate
04.024.030.00 30 kPa culture surface 24-well plate
04.024.100.00 100 kPa culture surface 24-well plate
Cover slips
Product Code Description
03.020.002.00 2 kPa culture surface 20x20 mm c.slip
03.020.005.00 5 kPa culture surface 20x20 mm c.slip
03.020.010.00 10 kPa culture surface 20x20 mm c.slip
03.020.015.00 15 kPa culture surface 20x20 mm c.slip
03.020.030.00 30 kPa culture surface 20x20 mm c.slip
 化工仪器网
化工仪器网









 化工仪器网
化工仪器网